Unlocking the Power of Structured Outputs in OpenAI and Azure OpenAI
Unlocking the Power of Structured Outputs in OpenAI and Azure OpenAI
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, staying ahead of the curve means embracing innovations that make technology more intuitive, reliable, and accessible. About a month ago, OpenAI introduced a groundbreaking feature to their API: structured outputs. The feature is available for the versions
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 and later
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06 and later
This advancement has quickly gained traction among developers and data scientists for its ability to produce consistent, machine-readable responses, streamlining the integration of AI into various applications.
Now, we’re thrilled to see that structured outputs are available in the Azure OpenAI Service as well. This integration brings the power of structured data to the Azure ecosystem, opening doors for more robust and efficient AI solutions within Azure’s secure and scalable environment.
What We’ll Cover
In this blog post, we’ll explore:
What Structured Outputs Are: Understanding the concept and significance of moving beyond unstructured text to predictable, formatted data.
How It Works: A look under the hood at how this feature operates within the OpenAI and Azure OpenAI APIs.
Why It’s a Big Deal: Discussing the transformative impact of structured outputs on AI development and deployment.
Practical Examples and Code: Providing hands-on examples to demonstrate how you can leverage structured outputs in your projects.
Let’s dive in and unlock the potential of structured outputs together!
1. What Are Structured Outputs?
At its core, a structured output allows AI models to return data in a well-defined format, such as JSON. Instead of receiving raw, free-form text, users can now request specific types of information from the model in a predictable format. For example, if you need a product recommendation, you can ask the model to respond in a JSON format containing structured fields like product name, price, and description.
Why Is This Important?
Before structured outputs, integrating AI-generated text into applications was cumbersome. Developers often had to write extra code to parse, clean, and validate the AI’s responses. A simple request like extracting a product’s name and price from a text response required complex parsing logic, which was error-prone and inconsistent. In some cases, models would deviate from the expected format, making it even harder to handle responses in real-time systems.
Structured outputs eliminate this guesswork. By specifying the exact format for a response—like a key-value pair or an array of objects—you ensure the data is always delivered in a way that your application can process without additional validation. This feature is crucial for applications that need consistent and reliable data.
2. Use Cases of Structured Outputs
Chatbots: Ensuring chatbot responses adhere to a predefined structure for improved conversation flow and decision-making.
Data Summarization: Summarizing complex documents in a machine-readable format for automated systems to use directly.
Web Scraping: A form of data summarization. When scraping websites, the data you get is often unstructured, requiring significant post-processing to format it for your system. With structured outputs, AI can process raw scraped data and directly return it in a well-defined structure, like JSON, saving you the effort of organizing it manually.
Structured outputs streamline the process of turning unstructured information from sources like web scraping into usable data without additional coding or post-processing.
3. How It Works
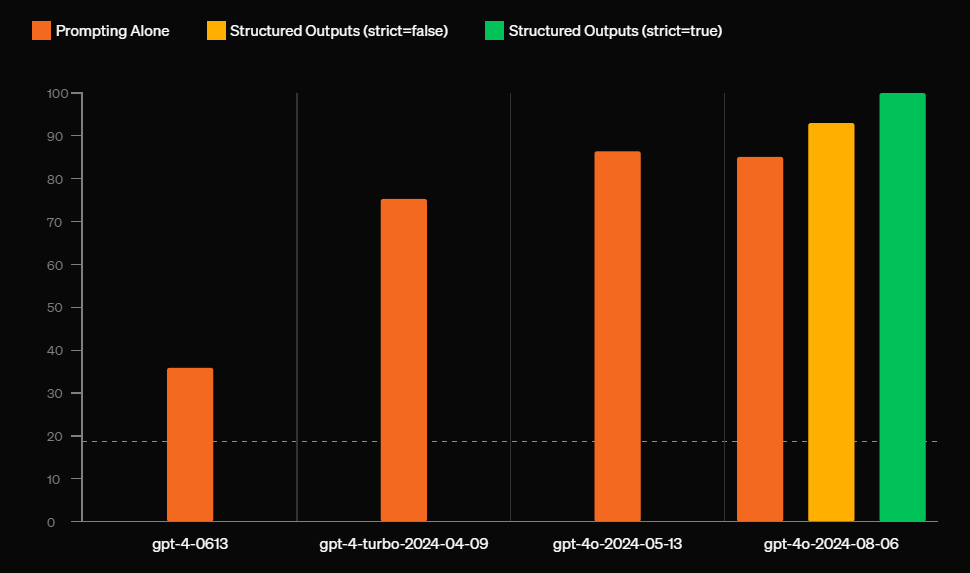
Achieving 100% reliable structured outputs in OpenAI is a remarkable feat, considering that AI models are inherently non-deterministic. Open AI employed a two-part strategy: first, they trained the GPT-4 model to understand complex schemas, which significantly improved the model’s output reliability. However, even with a 93% success rate, the randomness of model behavior remained an issue.
The real breakthrough came with the introduction of constrained decoding. without contrained decoding, the model is free to choose any token (like a { or a ,) at any time, which can lead to invalid outputs—especially when adhering to strict formats like JSON. With constrained decoding, OpenAI tackled this by dynamically restricting the model to generate only tokens that are valid according to the defined schema at each step.
Image source: openai.
How Does Constrained Decoding Work?
To ensure every token matches the required schema, OpenAI converts the JSON Schema into a context-free grammar, which essentially defines a set of rules that govern valid outputs. The model uses this grammar to guide its generation process, ensuring that only tokens valid at any given step are considered. For example, after generating an opening curly brace {, it restricts the model from producing another { until it’s logically valid based on the schema. This ensures that the generated output adheres exactly to the structure specified.
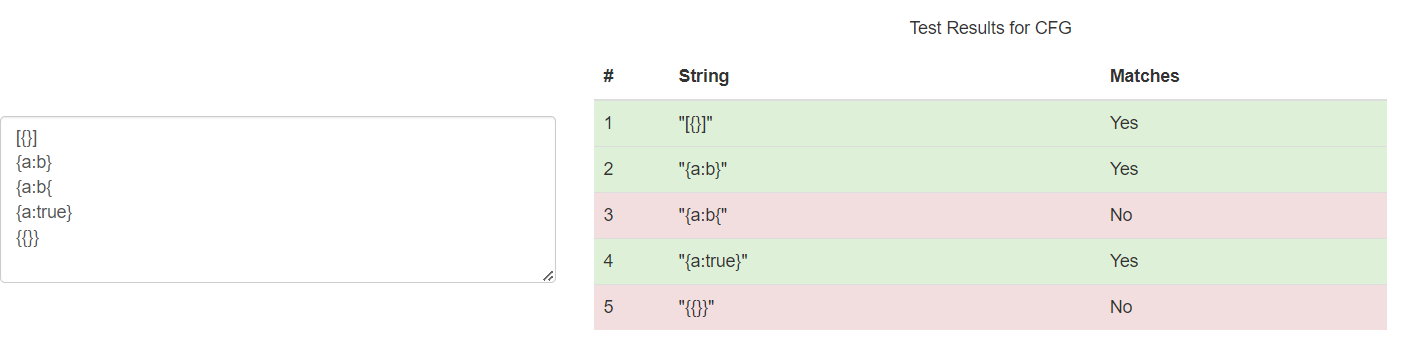 Illustration of Context free grammar matching
Illustration of Context free grammar matching
This process incurs a slight latency when handling new schemas, as the grammar needs to be precomputed. However, once processed, the system uses cached data to minimize any performance impact during actual generation. The ability to reliably generate structured outputs without manual validation is a significant improvement in model deployment, particularly in applications that require strict formatting like APIs, data pipelines, or enterprise systems.
This dynamic token validation is why OpenAI can guarantee 100% adherence to specified formats. It’s not just an impressive technical achievement, but a game changer for developers building AI-driven applications that need to rely on structured, predictable outputs.
This blend of AI learning and deterministic engineering is a big leap forward for reliable AI output in complex production environments.
Learn more about how this works from this aricle.
4. Why This Is a Big Deal
Before Structured Outputs
Before structured outputs, developers faced significant challenges integrating AI-generated responses into real-world applications. Models like GPT-3.5 produced free-form text, which, while useful for conversational AI, presented a problem when precise, machine-readable formats were required. For example, parsing AI responses for structured data, like JSON, often involved complex post-processing steps, including writing custom scripts and regex patterns. These steps were not only error-prone but added extra time and development effort to ensure the output fit into structured systems like databases, APIs, or spreadsheets.
Unpredictable formatting meant that developers had to account for a range of edge cases, such as missing fields, inconsistent syntax, or extra data that didn’t belong. This made it difficult to scale AI applications in environments that demanded reliable and structured information, which are most of the enterprise environments. For enterprise applications, this lack of consistency was a dealbreaker in many situations, requiring manual validation or extensive logic to clean and transform data into the desired format.
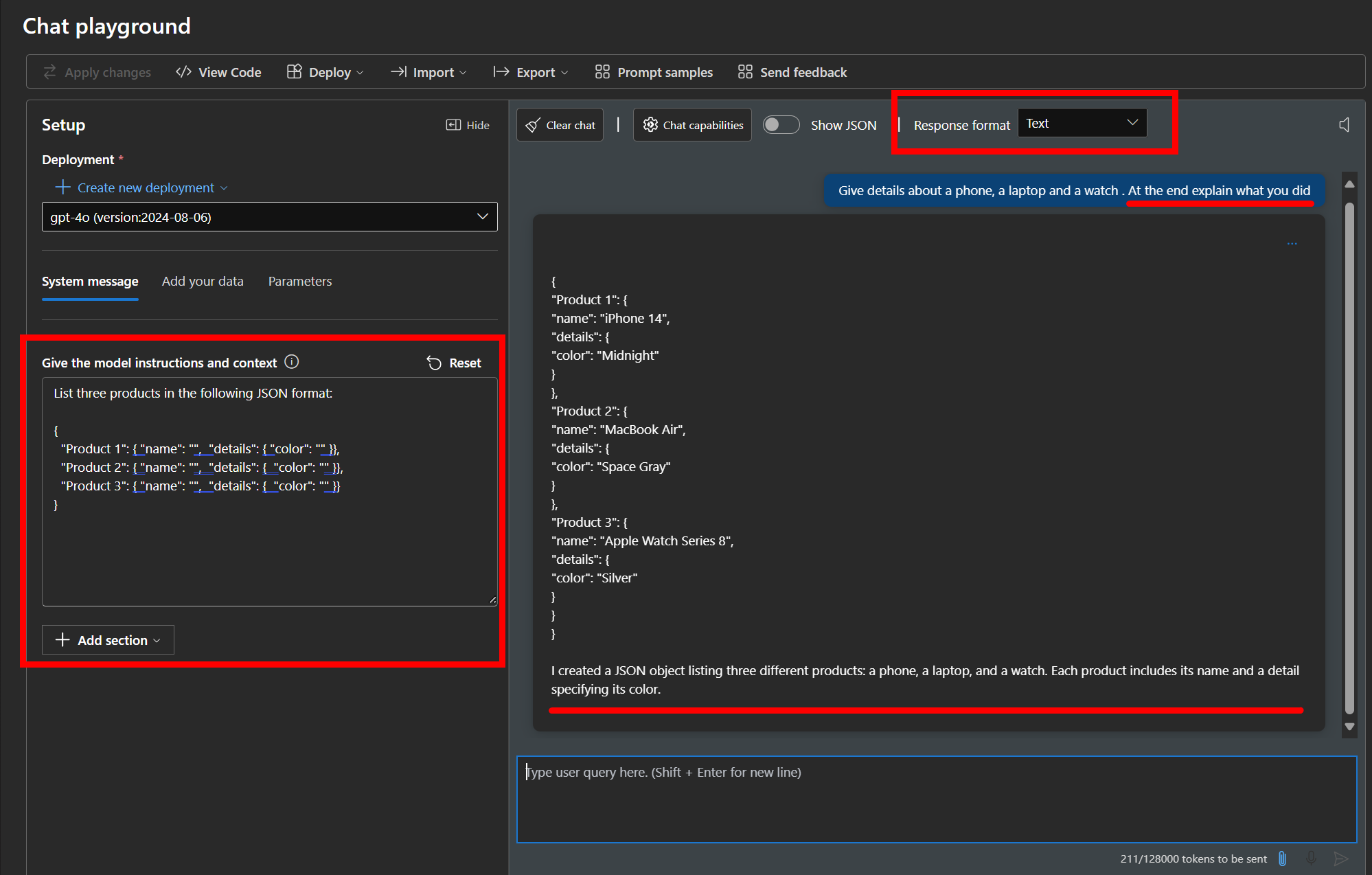 Before structured output - The output may not strictly follow the schema, the prompt can be made in a way that the output structure might differ.
Before structured output - The output may not strictly follow the schema, the prompt can be made in a way that the output structure might differ.
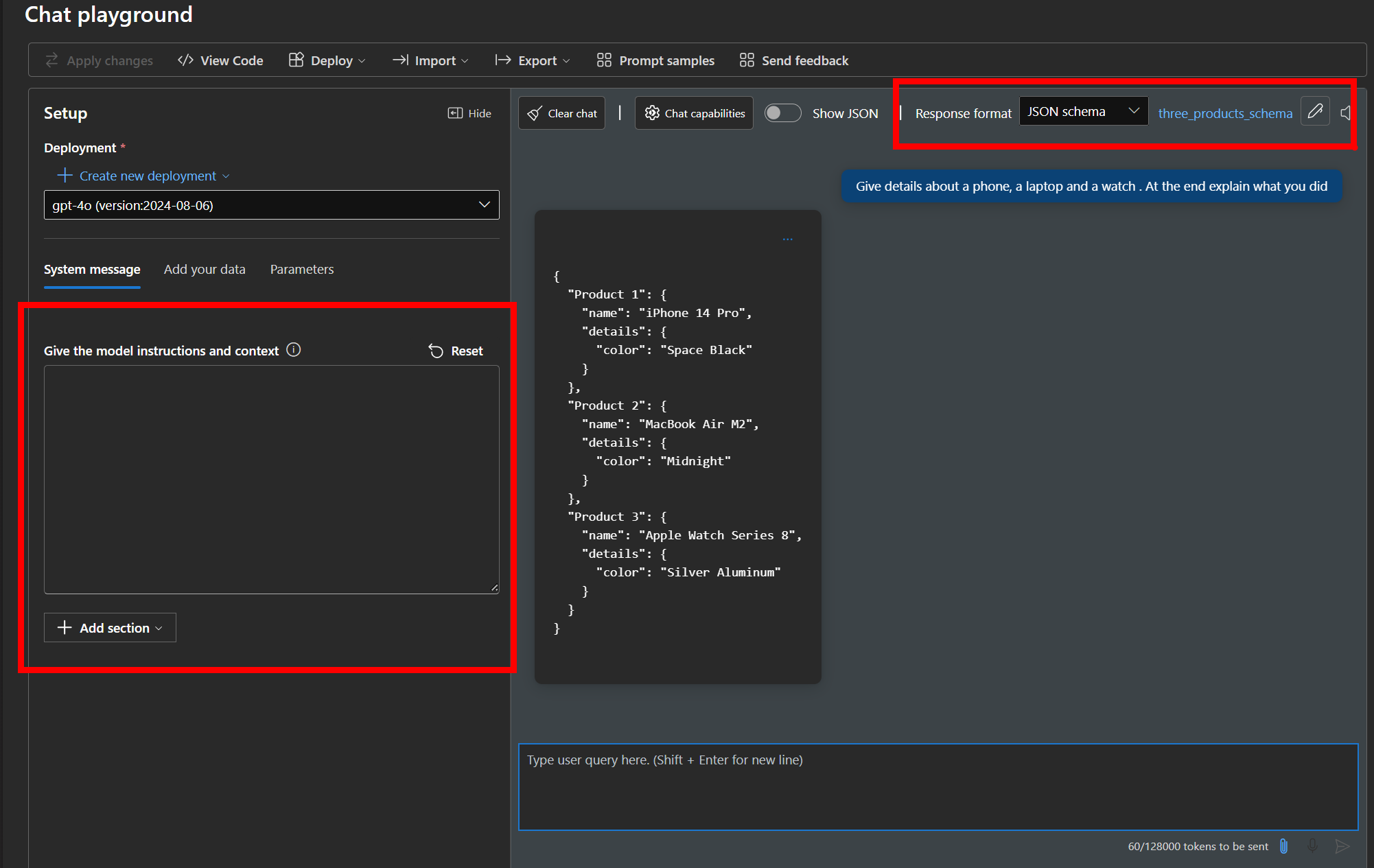 After structured output - The ouput strictly follows the schema even when the prompt says otherwise.
After structured output - The ouput strictly follows the schema even when the prompt says otherwise.
Real-World Impact
Structured outputs radically change this picture by ensuring AI responses follow a predictable format, which directly integrates with traditional software systems. This improvement simplifies development, eliminating the need for complex post-processing and validation steps. For instance, in a customer support application, structured outputs ensure the AI returns exactly the right fields—such as issue type, user data, and timestamp—so that the system can automatically file a support ticket without needing additional parsing.
This feature doesn’t just benefit developers—it also reduces operational risks and increases efficiency across the board. Companies can now confidently deploy AI models in enterprise environments.
5. Structured Outputs in Azure OpenAI
Recent Integration
With the recent addition of structured outputs in the Azure OpenAI Service, Microsoft has now extended OpenAI’s powerful new feature to its platform. This integration enables Azure developers to leverage OpenAI’s models that support structured outputs making it easier to build reliable applications within the Azure cloud.
Security and Compliance
Azure’s strength lies in its enterprise-grade security, and with structured outputs, this advantage becomes even more significant for industries that must comply with strict regulations. Data consistency plays a critical role in regulated industries, where structured outputs ensure that AI-generated data is always in the expected format, reducing the risk of data mishandling, errors, compliance breaches or prompt injection attacks.
For industries bound by standards such as HIPAA or GDPR, this feature provides extra reassurance that outputs are validated and constrained, minimizing any chance of inadvertently non-compliant or malformed data entering systems. The combination of structured outputs and Azure’s secure infrastructure makes this feature especially valuable for applications dealing with sensitive or mission-critical data.
6. Practical Examples and Code
Let’s look at a practical scenario to demonstrate how structured outputs make a significant difference in handling complex AI responses. We’ll use an example from the data summarization domain: summarizing a resume and returning structured data like name, email, work_experience, etc…
With structured outputs, the process is very streamlined. You define the schema upfront, and the model is constrained to only output valid JSON that matches the schema exactly, eliminating the need for post-processing or validation. You can either mention the schema using JSON-schema or Pydantic for Python and Zod for Javascript respectively.
Example With Structured Outputs:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from openai import AzureOpenAI
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential, get_bearer_token_provider
# Set up the token provider
token_provider = get_bearer_token_provider(
DefaultAzureCredential(), "https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/.default"
)
# Initialize Azure OpenAI client
client = AzureOpenAI(
azure_endpoint=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"),
azure_ad_token_provider=token_provider,
api_version="2024-08-01-preview"
)
# Define the Pydantic model for the structured response with field descriptions
class ResumeDetails(BaseModel):
class WorkExperience(BaseModel):
company: str = Field(description="The name of the company where the candidate worked.")
role: str = Field(description="The role or position the candidate held at the company.")
years: str = Field(description="The duration or years the candidate worked at the company.")
name: str = Field(description="The full name of the candidate.")
email: str = Field(description="The candidate's email address.")
phone: str = Field(description="The candidate's phone number.")
education: list[str] = Field(description="List of education qualifications, including degrees and institutions.")
work_experience: list[WorkExperience] = Field(description="List of work experiences, with details such as company, role, and duration.")
skills: list[str] = Field(description="List of the candidate's key skills.")
# The prompt and completion to parse the resume information
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model="MODEL_DEPLOYMENT_NAME", # replace with the actual model deployment name
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Extract the resume information."},
{"role": "user", "content": """
Johnathan Smith
Email: john.smith@domain.com
Phone: (555) 987-6543
Education:
- Master of Business Administration (MBA), Harvard Business School (2017-2019)
- Bachelor of Science in Computer Engineering, Stanford University (2013-2017)
Work Experience:
- Senior Product Manager at Microsoft (2020-2023)
- Led a cross-functional team of 20+ members to launch a new SaaS product, resulting in 15% market share growth.
- Spearheaded the implementation of agile methodologies, reducing development time by 25%.
- Managed a $10M product budget, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
- Product Manager at Open AI (2017-2020)
- Managed the end-to-end lifecycle of e-commerce solutions, leading to a 12% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Collaborated with engineering and marketing teams to define and launch new features.
Skills:
- Product Management
- Agile Methodologies
- Budget Management
- Cloud Computing (Azure, AWS)
- Team Leadership
- Python
- Data Analysis
- SQL
Certifications:
- Certified Scrum Master (CSM)
- Azure Certified Solutions Architect
"""
},
],
response_format=ResumeDetails,
)
# Extract the structured data
resume = completion.choices[0].message.parsed
# Print the parsed resume details
print(resume.model_dump_json(indent=2))
Example output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
{
"name": "Johnathan Smith",
"email": "john.smith@domain.com",
"phone": "(555) 987-6543",
"education": [
"Master of Business Administration (MBA), Harvard Business School (2017-2019)",
"Bachelor of Science in Computer Engineering, Stanford University (2013-2017)"
],
"work_experience": [
{
"company": "Microsoft",
"role": "Senior Product Manager",
"years": "2020-2023"
},
{
"company": "Open AI",
"role": "Product Manager",
"years": "2017-2020"
}
],
"skills": [
"Product Management",
"Agile Methodologies",
"Budget Management",
"Cloud Computing (Azure, AWS)",
"Team Leadership",
"Python",
"Data Analysis",
"SQL"
]
}
In this scenario, the AI is constrained by the schema during the generation process. No matter how complex the structure, the model will only output data that fits within the JSON schema and ignores other content. There’s no need to manually parse or validate the response—the output is guaranteed to be correct interms of the structure.
Structured outputs have simplified AI implementations dramatically, especially for complex tasks like data summarization. By eliminating unpredictable outputs, this feature ensures smoother integration and greater efficiency in real-world applications.
Conclusion
Structured outputs represent a leap forward for AI developers, offering significant benefits in time-saving, error reduction, and seamless integration. By ensuring that AI responses are always returned in a predictable, machine-readable format like JSON, developers can avoid the hassles of manual post-processing and focus on building reliable, efficient applications. This feature enhances machine-to-machine communication, making it easier to integrate AI models into real-world workflows.
Whether you’re using OpenAI or Azure OpenAI, try structured outputs in your next project. Get started by exploring OpenAI’s documentation or Azure’s guide today!